Theresa May has written to the European Union to request a further delay to Brexit until 30 June. Currently, it is scheduled to happen on 12 April.
5 April 2019
Under the prime minister's proposal Brexit could still happen earlier if a deal is ratified. An emergency EU summit will be held on 10 April where the request will be considered.


Government ministers are also continuing talks with Labour leaders to try to find a compromise deal. If they can agree, MPs will be given a chance to vote on the deal. If not, a range of alternative options will be put to them instead.
In either case, the prime minister says the negotiated withdrawal agreement would remain unchanged. That's the legally binding part of the Brexit deal that covers exit terms - including money, the transition period, citizen's rights and the border between Northern Ireland and the Republic.
There could be changes to the non-legally binding political declaration which sets out parameters for the long-term future relationship. Or new commitments on Britain's future negotiating objectives could be written into legislation.
The vote could happen before the 10 April summit but it is perhaps more likely now that it will be afterwards.
There is a possibility at the summit that the EU will suggest a different length for any extension - they could suggest a longer or a shorter delay.
Then the UK would have to weigh up the offer. To add to the complication, it might be up to MPs to decide - if a new law proposed by Yvette Cooper, and backed by MPs on 3 April, gets through the House of Lords as well.
If the compromise plan does not yield results, many things could happen.
1. No deal
No-deal Brexit is still the default outcome if MPs can't agree anything else and there are no further extensions.
As things stand a no-deal Brexit would happen on 12 April in the absence of any other decisions.
It could also still happen at a later date if any further extension fails to break the deadlock.
2. Leave the EU on the PM's deal
Despite the repeated rejection of Theresa May's deal, it has not been permanently ruled out.
Even now, if a compromise cannot be agreed with the Labour leader, and if there is no majority among MPs for an alternative, it remains a possibility.
And in the event of a longer Brexit delay, the negotiated deal could come back at a later date as a way of allowing an early exit.
Also, if negotiations with the EU on any alternative plan run into difficulties, the two sides could decide to return to the one deal that has been fully worked out.
3. Major renegotiation
The government could choose to negotiate a completely new Brexit deal.
This wouldn't be a question of making small additions to the political declaration.
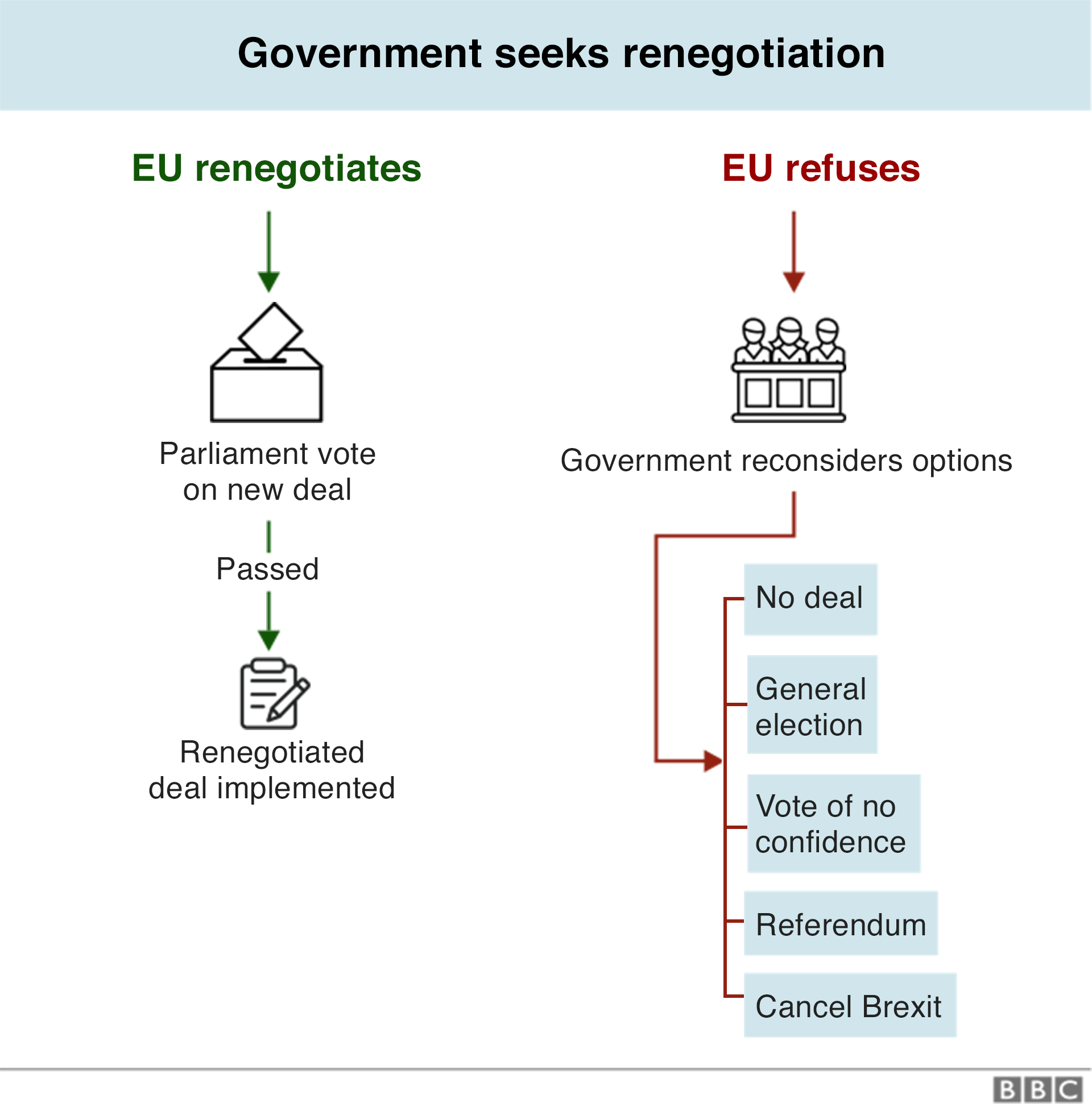

Instead, there could be a complete renegotiation that would take some time - probably involving a rewrite of the withdrawal agreement. It would require a long delay to Brexit and the UK would have to take part in the European Parliament elections in May.
If the EU refused to re-enter negotiations, the government would have to plump for one of the other options instead.
4. Another referendum
A further possibility is to hold another referendum.
It could have the same status as the 2016 referendum, which was legally non-binding and advisory. But some MPs want to hold a binding referendum where the result would automatically take effect - like with the 2011 referendum on changing the voting system for UK general elections.
Either way, a referendum can't just happen automatically. The rules for referendums are set out in a law called the Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000.
There would have to be a new piece of legislation to make a referendum happen and to determine the rules, such as who would be allowed to vote.
It couldn't be rushed through, because there has to be time for the Electoral Commission to consider and advise on the referendum question.
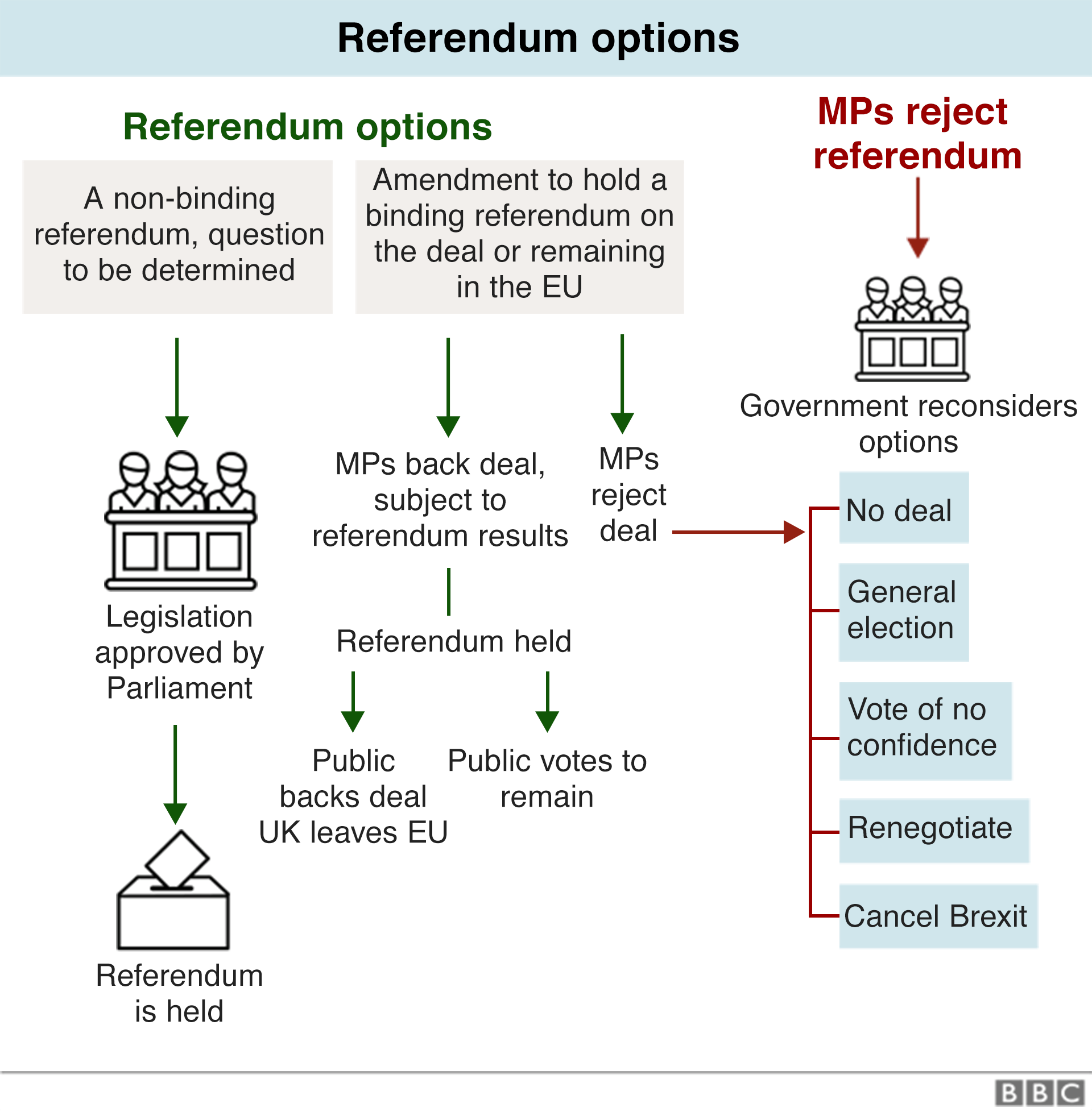

The question is then defined in the legislation.
Once the legislation has been passed, the referendum couldn't happen immediately either. There would have to be a statutory "referendum period" before the vote takes place.
Experts at University College London's Constitution Unit suggest that the minimum time for all of the required steps above is about 22 weeks.
5. Call a general election
Theresa May could decide the best way out of the deadlock would be to hold an early general election.
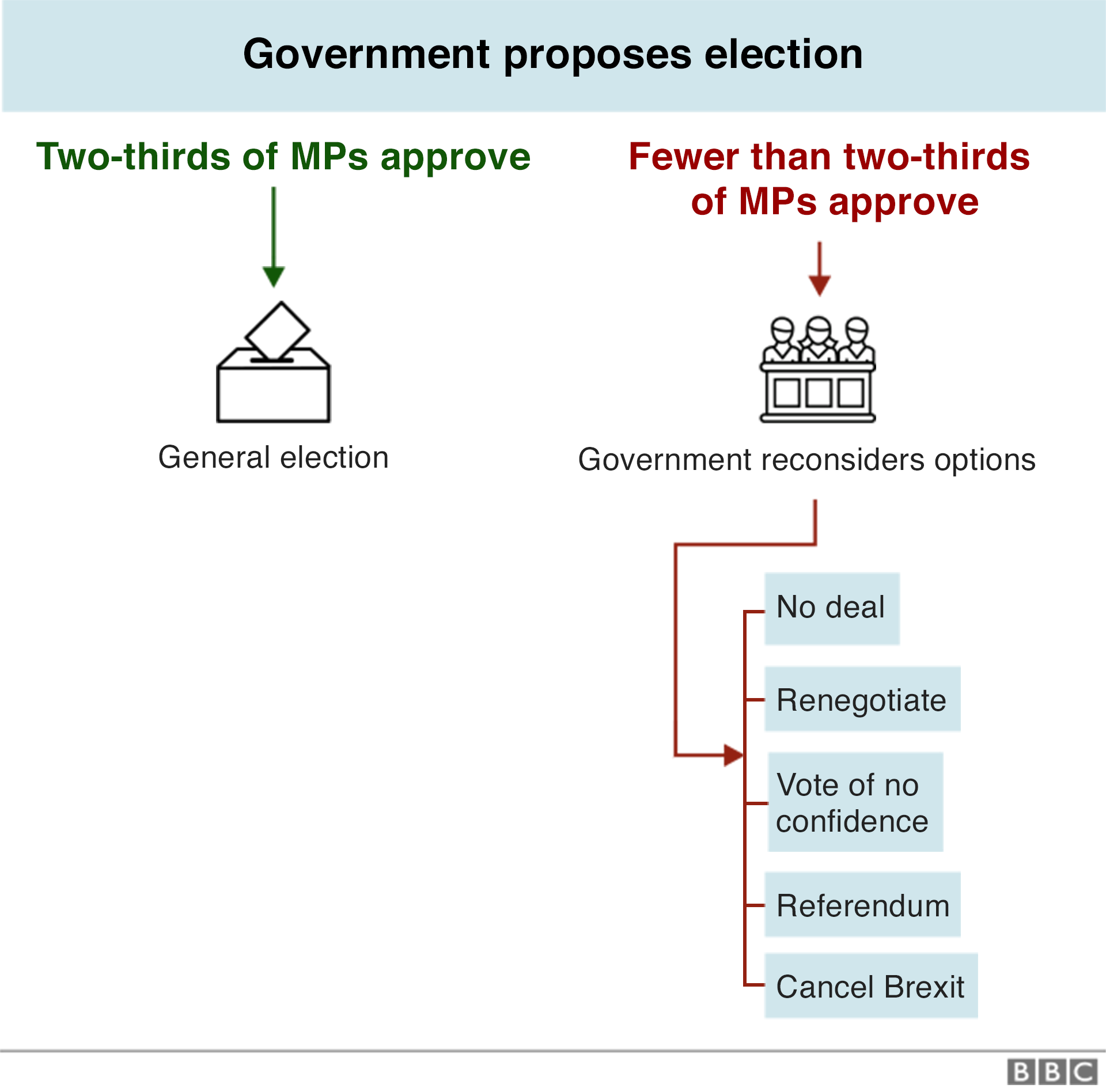

She doesn't have the power just to call an election. But, as in 2017, she could ask MPs to vote for an early election under the terms of the Fixed Term Parliaments Act.
Two-thirds of all MPs would need to support the move. The earliest date for the election would be 25 working days later but it could be after that - the prime minister would choose the precise date.
6. Another no-confidence vote
The government survived a vote of no confidence on 16 January by 325 votes to 306. Labour could table another no confidence motion at any time.
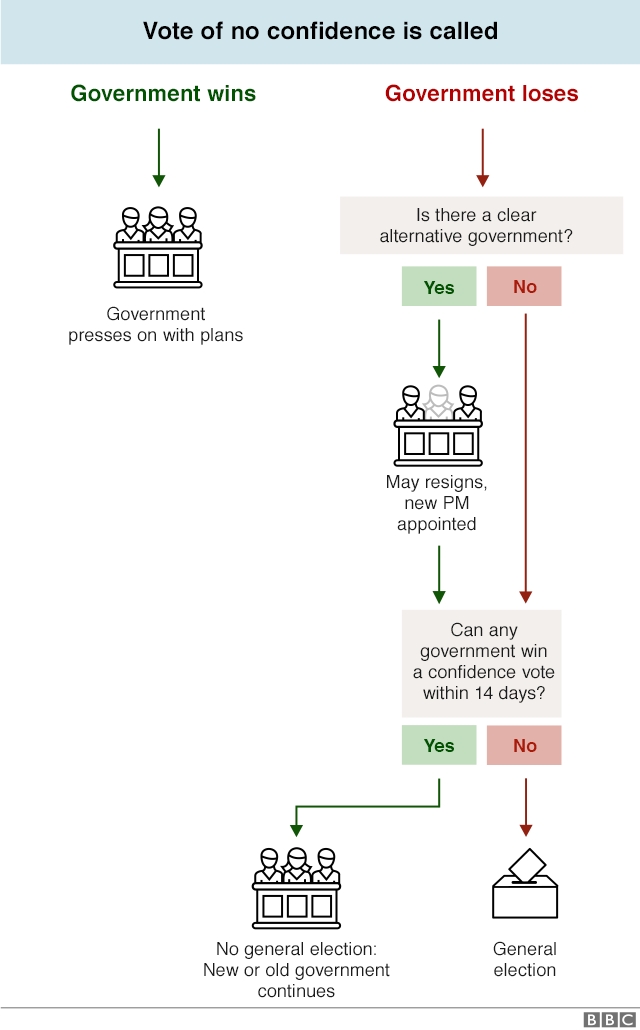

Under the Fixed Term Parliaments Act 2011, UK general elections are only supposed to happen every five years. The next one is due in 2022.
But a vote of no confidence lets MPs vote on whether they want the government to continue. The motion must be worded: "That this House has no confidence in Her Majesty's Government."
If a majority of MPs vote for the motion then it starts a 14-day countdown.
If during that time the current government or any other alternative government cannot win a new vote of confidence, then an early general election would be called.
That election cannot happen for at least 25 working days.
7. No Brexit
The European Court of Justice has ruled that it would be legal for the UK to unilaterally revoke Article 50 to cancel Brexit (without the need for agreement from the other 27 EU countries).
With the government still committed to Brexit, it's very likely that a major event such as a further referendum or change of government would have to happen before such a move.
However, any further delay to Brexit would certainly lead to questions about whether the ultimate destination was going to be a reversal of the 2016 referendum.
It's not totally clear what the process would be. But an act of Parliament calling for Article 50 to be revoked would probably be sufficient.
Other possibilities
Theresa May has said she will step down if her deal is passed.
Having already survived a challenge to her leadership, there is no way she can be forced out by her party until December - under the Conservative Party rules.
But she could still choose to resign if she can't get her deal through and she's not prepared to change course.
That would trigger a Conservative leadership campaign which would result in the appointment of a new prime minister.
She might also come under pressure to resign if MPs pass a "censure motion" - that would be a bit like a no-confidence vote but without the same automatic consequences. Again this could lead to a change in prime minister or even a change in government.
Whoever ended up in charge would still face the same basic range of Brexit options though.